sp_index_visual – A tabular visualization of a table’s columns and if they are indexed
During some SQL development, I ran into an instance where I wanted to evaluate the existing indexes on a table to see if any of them nearly covered my query. Additionally, given a large number of existing indexes on the table, I figured I might be removing/consolidating some. I’m very visual, so opening each index individually didn’t seem to help me track which columns were used in which index. Enter sp_index_visual.
The whole project is now stored on GitHub , but I’m going to run through the meat and potatoes.
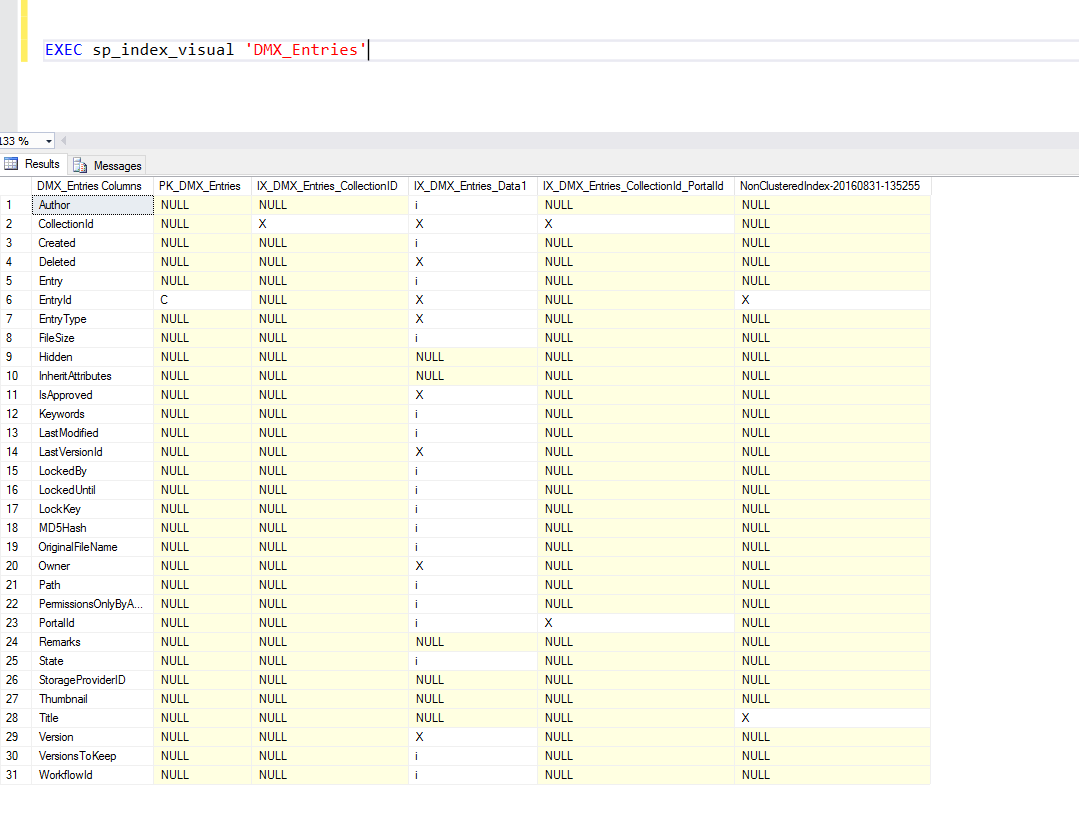
After adding the stored procedure to a database, you can run it with the table name as the sole parameter to obtain a breakdown of the indexes on the table.
- C = clustered index
- X = unclustered index
- i = included column
[sql]
-- sp_index_visual
-- 2/13/2017
-- drewsk.tech
CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.sp_index_visual
@INQTABLE NVARCHAR(100)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE @COLUMNS NVARCHAR(MAX)
DECLARE @QSQL NVARCHAR(MAX)
SET @COLUMNS = STUFF((SELECT ', [' + NAME + '] ' FROM
( select ind.name
from sys.tables t
left JOIN sys.indexes ind ON ind.object_id = t.object_id
WHERE t.name = @INQTABLE) TUF
FOR XML PATH(''), TYPE
).value('.', 'NVARCHAR(MAX)')
,1,1,'')
set @QSQL = 'select *
from
(
select
ind.name as indexname,
tcol.name as ['+@INQTABLE+' Columns],
case when ic.is_included_column = 0 then
case when ind.type = 1 then ''C'' else ''X'' end
else ''i'' end as columnused
from sys.tables t
INNER JOIN sys.columns tcol on t.object_id = tcol.object_id
left JOIN sys.index_columns ic ON t.object_id = ic.object_id and ic.column_id = tcol.column_id --and ic.is_included_column = 0
left JOIN sys.columns col ON ic.object_id = col.object_id and ic.column_id = col.column_id
left JOIN sys.indexes ind ON ind.object_id = t.object_id and ind.index_id = ic.index_id
WHERE t.name = N'''+@INQTABLE+'''
) indecies
PIVOT
(
max(columnused)
for indexname IN ('+@COLUMNS+')
) as pivottable;'
EXECUTE(@QSQL)
END
GO[sql]
There are lots of options to improve the procedure further in the future:
- drop if exists
- order indexes by clustered, # of columns, etc
- display uniqueness constraints
- display foreign keys